一、总结前置:
1、ribbon、feign、openfeign三者的对比:
我们现在工作中现在几乎都是直接使用openfeign,而我们很有必要了解一下,ribbon、feign、openfeign三者之间的关系!
-
ribbon:ribbon是netflix开源的客户端负载均衡组件,可以调用注册中心获取服务列表,并通过负载均衡算法挑选一台Server;
-
feign:feign也是netflix开源的,是对ribbon的一层封装,通过接口的方式使用,更加优雅,不需要每次都去写restTemplate,只需要定义一个接口来使用;但是Feign不支持springmvc的注解;
-
openfeign:是对feign的进一步封装,使其能够支持springmvc注解,如@GetMapping等,使用起来更加方便和优雅!
2、工作中都是如何使用openfeign:
// 想要使用openfeign,必须要在启动类增加@EnableFeignClient注解,否则启动报错
@FeignClient("feign-provider")
public interface OrderService {
@GetMapping("/order/get/{id}")
public String getById(@PathVariable("id") String id);
}
3、openfeign与ribbon如何分工?
-
1. openfeign通过动态代理的方式,对feignclient注解修饰的类进行动态代理,拼接成临时URL:http://feign-provider/order/get/100,交给ribbon
-
2. ribbon通过自己的拦截器,截取出serviceName在服务注册表中找到对应的serverList,并通过负载均衡策略挑选一台Server,拼接成最终的URL:http://10.206.73.156:1111/order/get/100,交还给feign;
-
3. 最后,feign通过自己封装的Client对目标地址发起调用,并获得返回结果;(Client是对原生 java.net 中的URL类的封装,实现远程调用)
二、核心代码——Openfeign生成的动态代理类是啥?(LoadBalancerFeignClient.class)
1、启动类必须增加@EnableFeignClient,那我们就从这里入口:
@EnableFeignClients
|
|
@Import(FeignClientsRegistrar.class)
|
|
// 遇到import(Registrar),我们就去看它的registerBeanDefinitions()方法:
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata,
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
registerDefaultConfiguration(metadata, registry);
// 注册FeignClient,其实FeignClient就是我们需要的动态代理类
registerFeignClients(metadata, registry);
}
|
|
public void registerFeignClients(AnnotationMetadata metadata,BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
......
// 定义过滤器,把加了@FeignClient注解的接口都过滤出来
AnnotationTypeFilter annotationTypeFilter = new AnnotationTypeFilter(FeignClient.class);
...过滤逻辑...
for (String basePackage : basePackages) {
Set<BeanDefinition> candidateComponents = scanner
.findCandidateComponents(basePackage);
for (BeanDefinition candidateComponent : candidateComponents) {
if (candidateComponent instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {
// verify annotated class is an interface
AnnotatedBeanDefinition beanDefinition = (AnnotatedBeanDefinition) candidateComponent;
AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata = beanDefinition.getMetadata();
Assert.isTrue(annotationMetadata.isInterface(),
"@FeignClient can only be specified on an interface");
Map<String, Object> attributes = annotationMetadata
.getAnnotationAttributes(
FeignClient.class.getCanonicalName());
String name = getClientName(attributes);
registerClientConfiguration(registry, name,
attributes.get("configuration"));
// 将为每一个过滤出来的接口,注册FeignClient
registerFeignClient(registry, annotationMetadata, attributes);
}
}
}
}
|
|
private void registerFeignClient(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry,
AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata, Map<String, Object> attributes) {
String className = annotationMetadata.getClassName();
BeanDefinitionBuilder definition = BeanDefinitionBuilder
.genericBeanDefinition(FeignClientFactoryBean.class);
...目标FactoryBean为FeignClientFactoryBean...
...FactoryBean一般用于定制化一些特殊的Bean,spring会调用它的getObject接口...
BeanDefinitionHolder holder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDefinition, className,
new String[] { alias });
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(holder, registry);
}
2、见名知意FeignClient的工厂bean:FeignClientFactoryBean.getObject()方法:
class FeignClientFactoryBean{
@Override
public Object getObject() throws Exception {
return getTarget();
}
<T> T getTarget() {
FeignContext context = this.applicationContext.getBean(FeignContext.class);
Feign.Builder builder = feign(context);
// 当我们不为@FeignClient()注解配置url属性时
// 这里同时会根据注解,拼接出url前缀,如:http://feign-provider
if (!StringUtils.hasText(this.url)) {
if (!this.name.startsWith("http")) {
this.url = "http://" + this.name;
}
else {
this.url = this.name;
}
this.url += cleanPath();
return (T) loadBalance(builder, context,
new HardCodedTarget<>(this.type, this.name, this.url));
}
...如果我们为@FeignClient()注解配置url属性之后的逻辑...
}
}
|
|
protected <T> T loadBalance(Feign.Builder builder, FeignContext context,
HardCodedTarget<T> target) {
// 从容器中获取一个类型为Client的bean,那么IOC容器中肯定有一个这样的Bean
Client client = getOptional(context, Client.class);
if (client != null) {
builder.client(client);
Targeter targeter = get(context, Targeter.class);
return targeter.target(this, builder, context, target);
}
// 如果找不到类型为Client的Bean就是有问题的啦!
throw new IllegalStateException(
"No Feign Client for loadBalancing defined. Did you forget to include spring-cloud-starter-netflix-ribbon?");
}
3、容器中类型为Client的Bean是谁?
此时还是启动阶段,我们去看看有哪些bean会被注入,在 spring.factories 中,我们会找到两个自动配置类:
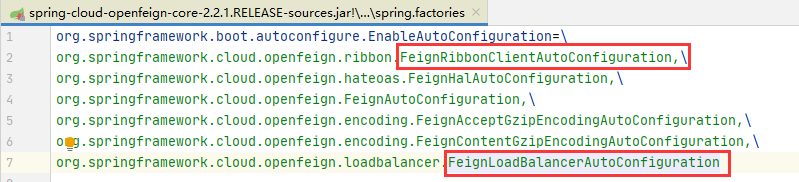
这两个类,很关键,都会往容器中注入负载均衡的Client Bean,但是只会有一个成功,
FeignRibbonClientAutoCOnfiguration类:
@ConditionalOnClass({ ILoadBalancer.class, Feign.class })
@ConditionalOnProperty(value = "spring.cloud.loadbalancer.ribbon.enabled",
matchIfMissing = true)
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
// 重点1:在FeignAutoConfiguration之前装载配置
@AutoConfigureBefore(FeignAutoConfiguration.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ FeignHttpClientProperties.class })
@Import({ HttpClientFeignLoadBalancedConfiguration.class,
OkHttpFeignLoadBalancedConfiguration.class,
DefaultFeignLoadBalancedConfiguration.class }) // 重点2:
public class FeignRibbonClientAutoConfiguration {
...非重点...
}
|
|
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
class DefaultFeignLoadBalancedConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean // 如果Client类型的bean已经存在,则不执行
public Client feignClient(CachingSpringLoadBalancerFactory cachingFactory,
SpringClientFactory clientFactory) {
return new LoadBalancerFeignClient(new Client.Default(null, null), cachingFactory,
clientFactory);
}
}
FeignLoadBalancerAutoConfiguration类:
@ConditionalOnClass(Feign.class)
@ConditionalOnBean(BlockingLoadBalancerClient.class)
@AutoConfigureBefore(FeignAutoConfiguration.class)
// 重点1:在FeignRibbonClientAutoConfiguration之后装载配置
@AutoConfigureAfter(FeignRibbonClientAutoConfiguration.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(FeignHttpClientProperties.class)
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Import({ HttpClientFeignLoadBalancerConfiguration.class,
OkHttpFeignLoadBalancerConfiguration.class,
DefaultFeignLoadBalancerConfiguration.class }) // 重点2:
public class FeignLoadBalancerAutoConfiguration {
...非重点...
}
|
|
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
class DefaultFeignLoadBalancerConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean // 如果Client类型的bean已经存在,则不执行
public Client feignClient(BlockingLoadBalancerClient loadBalancerClient) {
return new FeignBlockingLoadBalancerClient(new Client.Default(null, null),
loadBalancerClient);
}
}
到这里就非常清晰了:
1. 通过spring.factories注入了两个配置类,并通过 @AutoConfigureBefore 和 @AutoConfigureAfter强制了两个配置类的装载顺序!
2. 这两个配置类各import 了 另一个配置类:DefaultFeignLoadBalancedConfiguration(注入:LoadBalancerFeignClient) 和 DefaultFeignLoadBalancerConfiguration(注入:FeignBlockingLoadBalancerClient),但是由于@ConditionalOnMissingBean注解,只有一个前面那个会注入成功!
所以,结论就是:IOC容器中的“Client”类型的 Bean 为 “LoadBalancerFeignClient”
所以,最终的结论就是:Openfeign通过的动态代理,为每个“@FeignClient”注解修饰的接口生成一个类型为 “LoadBalancerFeignClient”的代理类。
三、FeignClient代理类执行时,是如何使用Ribbon的?
1、当执行LoadBalancerFeignClient.execute()方法时:
// org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.ribbon.LoadBalancerFeignClient#execute
public Response execute(Request request, Request.Options options) throws IOException {
try {
URI asUri = URI.create(request.url());
String clientName = asUri.getHost();
URI uriWithoutHost = cleanUrl(request.url(), clientName);
FeignLoadBalancer.RibbonRequest ribbonRequest = new FeignLoadBalancer.RibbonRequest(
this.delegate, request, uriWithoutHost);
// 可以获取到nacos的一些信息
IClientConfig requestConfig = getClientConfig(options, clientName);
// lbClient(clientName):可以获得具体的代理类,每个@FeignClient修饰的接口代理类时独立的
return lbClient(clientName)
.executeWithLoadBalancer(ribbonRequest, requestConfig).toResponse();
}
catch (ClientException e) {
......
}
}
我们可以很清楚的看到,这里肯定会要用到Ribbon;
2、通过负载均衡器,执行调用,并返回结果:
// com.netflix.client.AbstractLoadBalancerAwareClient#executeWithLoadBalancer(...)
public T executeWithLoadBalancer(final S request, final IClientConfig requestConfig) throws ClientException {
LoadBalancerCommand<T> command = buildLoadBalancerCommand(request, requestConfig);
try {
return command.submit( // 这步会返回具体的,负载均衡选定好的Server
new ServerOperation<T>() {
@Override
public Observable<T> call(Server server) { // submit选好的Server作为入参
URI finalUri = reconstructURIWithServer(server, request.getUri());
S requestForServer = (S) request.replaceUri(finalUri);
try {
return Observable.just(AbstractLoadBalancerAwareClient.this.execute(requestForServer, requestConfig));
}
catch (Exception e) {
return Observable.error(e);
}
}
})
.toBlocking()
.single();
} catch (Exception e) {
......
}
}
|
|
// com.netflix.loadbalancer.reactive.LoadBalancerCommand#submit
public Observable<T> submit(final ServerOperation<T> operation) {
final ExecutionInfoContext context = new ExecutionInfoContext();
......
final int maxRetrysSame = retryHandler.getMaxRetriesOnSameServer();
final int maxRetrysNext = retryHandler.getMaxRetriesOnNextServer();
// selectServer()方法会通过负载均衡选择一台Server
Observable<T> o = (server == null ? selectServer() : Observable.just(server))
.concatMap(new Func1<Server, Observable<T>>() {
......
});
}
3、selectServer()具体方法:
// com.netflix.loadbalancer.reactive.LoadBalancerCommand#selectServer
private Observable<Server> selectServer() {
return Observable.create(new OnSubscribe<Server>() {
@Override
public void call(Subscriber<? super Server> next) {
try {
Server server = loadBalancerContext.getServerFromLoadBalancer(loadBalancerURI, loadBalancerKey);
next.onNext(server);
next.onCompleted();
} catch (Exception e) {
next.onError(e);
}
}
});
}
4、这里将使用到非常重要的一个ZoneAwareLoadBalancer:
// com.netflix.loadbalancer.LoadBalancerContext#getServerFromLoadBalancer
public Server getServerFromLoadBalancer(@Nullable URI original, @Nullable Object loadBalancerKey) throws ClientException {
String host = null;
int port = -1;
if (original != null) {
host = original.getHost();
}
if (original != null) {
Pair<String, Integer> schemeAndPort = deriveSchemeAndPortFromPartialUri(original);
port = schemeAndPort.second();
}
// 关键一步,获得了一个ILoadBalancer
ILoadBalancer lb = getLoadBalancer();
if (host == null) {
// 重要:这里其实获得的是ZoneAwareLoadBalancer类的Bean
if (lb != null){
Server svc = lb.chooseServer(loadBalancerKey);
if (svc == null){
throw new ClientException(ClientException.ErrorType.GENERAL,
"Load balancer does not have available server for client: "
+ clientName);
}
host = svc.getHost();
return svc;
} else {
......
}
} else {
......
}
return new Server(host, port);
}
|
|
// com.netflix.loadbalancer.BaseLoadBalancer#chooseServer
public Server chooseServer(Object key) {
if (!ENABLED.get() || getLoadBalancerStats().getAvailableZones().size() <= 1) {
logger.debug("Zone aware logic disabled or there is only one zone");
return super.chooseServer(key);
}
...其它分支在国内一般不会走,没有zone的概念...
}
|
|
// com.netflix.loadbalancer.BaseLoadBalancer#chooseServer
public Server chooseServer(Object key) {
if (counter == null) {
counter = createCounter();
}
counter.increment();
if (rule == null) {
return null;
} else {
try {
return rule.choose(key); // PredicateBasedRule
} catch (Exception e) {
return null;
}
}
}
|
|
// com.netflix.loadbalancer.PredicateBasedRule#choose
public Server choose(Object key) {
ILoadBalancer lb = getLoadBalancer();
Optional<Server> server = getPredicate().chooseRoundRobinAfterFiltering(lb.getAllServers(), key);
if (server.isPresent()) {
return server.get();
} else {
return null;
}
}
5、可以看到 lb.getAllServer(),正是ZoneAwareLoadBalancer.getAllServers()方法:
// com.netflix.loadbalancer.BaseLoadBalancer#getAllServers
public class BaseLoadBalancer extends AbstractLoadBalancer {
protected volatile List<Server> allServerList = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<Server>());
public List<Server> getAllServers() {
return Collections.unmodifiableList(allServerList);
}
}
所以,我们现在用弄清楚的有两点:
-
为什么重要的ILoadBalancer的实现就是ZoneAwareLoadBalancer;
-
ZoneAwareLoadBalancer中的allServerList属性是何时被赋值的;
四、ZoneAwareLoadBalancer是何时注入的?
1、在spring-cloud-netfliex-ribbon包的spring.factories中有RibbonAutoConfiguration类:
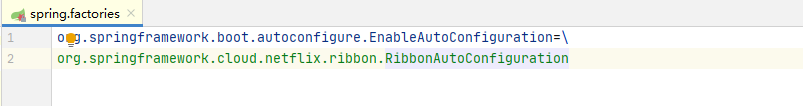
我们看到这个类的构造方法,创建了一个SpringClientFactory工厂类:
@Configuration
@Conditional(RibbonAutoConfiguration.RibbonClassesConditions.class)
@RibbonClients
@AutoConfigureAfter(
name = "org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EurekaClientAutoConfiguration")
@AutoConfigureBefore({ LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration.class,
AsyncLoadBalancerAutoConfiguration.class })
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ RibbonEagerLoadProperties.class,
ServerIntrospectorProperties.class })
public class RibbonAutoConfiguration {
@Autowired(required = false)
private List<RibbonClientSpecification> configurations = new ArrayList<>();
@Autowired
private RibbonEagerLoadProperties ribbonEagerLoadProperties;
@Bean
public HasFeatures ribbonFeature() {
return HasFeatures.namedFeature("Ribbon", Ribbon.class);
}
@Bean
public SpringClientFactory springClientFactory() {
// SpringClientFactory这个Client工厂类很关键
SpringClientFactory factory = new SpringClientFactory();
factory.setConfigurations(this.configurations);
return factory;
}
}
我们再看看这个工厂类的构造方法做了什么事:
public class SpringClientFactory extends NamedContextFactory<RibbonClientSpecification> {
static final String NAMESPACE = "ribbon";
public SpringClientFactory() {
super(RibbonClientConfiguration.class, NAMESPACE, "ribbon.client.name");
}
}
|
|
public abstract class NamedContextFactory<C extends NamedContextFactory.Specification> implements DisposableBean, ApplicationContextAware {
private final String propertySourceName;
private final String propertyName;
private Map<String, AnnotationConfigApplicationContext> contexts = new ConcurrentHashMap();
private Map<String, C> configurations = new ConcurrentHashMap();
private ApplicationContext parent;
private Class<?> defaultConfigType;
public NamedContextFactory(Class<?> defaultConfigType, String propertySourceName, String propertyName) {
this.defaultConfigType = defaultConfigType;
this.propertySourceName = propertySourceName;
this.propertyName = propertyName;
}
}
显然,构造了一个上下工厂“NamedContextFactory”类,这个工厂类的默认配置类是“RibbonClientConfiguraion”,这个在之后Feign的调用过程中非常关键;
2、LoadBalancerFeignClient这个代理类的execute()方法中:
// org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.ribbon.LoadBalancerFeignClient#execute
public Response execute(Request request, Request.Options options) throws IOException {
try {
URI asUri = URI.create(request.url());
String clientName = asUri.getHost();
URI uriWithoutHost = cleanUrl(request.url(), clientName);
FeignLoadBalancer.RibbonRequest ribbonRequest = new FeignLoadBalancer.RibbonRequest(
this.delegate, request, uriWithoutHost);
// 这个方法不用讲,得到的IclientConfig肯定是RibbonClientConfiguraion
IClientConfig requestConfig = getClientConfig(options, clientName);
return lbClient(clientName)
.executeWithLoadBalancer(ribbonRequest, requestConfig).toResponse();
}
catch (ClientException e) {
......
}
}
|
|
// org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.ribbon.LoadBalancerFeignClient#getClientConfig
IClientConfig getClientConfig(Request.Options options, String clientName) {
......
requestConfig = this.clientFactory.getClientConfig(clientName);
......
}
|
|
// org.springframework.cloud.netflix.ribbon.SpringClientFactory#getClientConfig
public IClientConfig getClientConfig(String name) {
return getInstance(name, IClientConfig.class);
}
|
|
// org.springframework.cloud.netflix.ribbon.SpringClientFactory#getInstance
public <C> C getInstance(String name, Class<C> type) {
// SpringClientFactory的super父类就是NamedContextFactory
C instance = super.getInstance(name, type);
if (instance != null) {
return instance;
}
IClientConfig config = getInstance(name, IClientConfig.class);
return instantiateWithConfig(getContext(name), type, config);
}
|
|
// org.springframework.cloud.context.named.NamedContextFactory#getInstance
public <T> T getInstance(String name, Class<T> type) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = this.getContext(name);
return BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(context, type).length > 0 ? context.getBean(type) : null;
}
找到了NamedContextFactory,就和第一点串起来了,它的默认配置类正是RibbonClientConfiguration;
3、RibbonClientConfiguration又是如何注入我们需要的ZoneAwareLoadBalancer的:
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@EnableConfigurationProperties
// Order is important here, last should be the default, first should be optional
// see
// https://github.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-netflix/issues/2086#issuecomment-316281653
@Import({ HttpClientConfiguration.class, OkHttpRibbonConfiguration.class,
RestClientRibbonConfiguration.class, HttpClientRibbonConfiguration.class })
public class RibbonClientConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public ILoadBalancer ribbonLoadBalancer(IClientConfig config,
ServerList<Server> serverList, ServerListFilter<Server> serverListFilter,
IRule rule, IPing ping, ServerListUpdater serverListUpdater) {
if (this.propertiesFactory.isSet(ILoadBalancer.class, name)) {
return this.propertiesFactory.get(ILoadBalancer.class, config, name);
}
// 默认注入的类正是ZoneAwareLoadBalancer
return new ZoneAwareLoadBalancer<>(config, rule, ping, serverList,
serverListFilter, serverListUpdater);
}
}
所以,这就解释了,为什么在后面的 ILoadBalancer lb = getLoadBalancer(); 获得到的就是ZoneAwareLoadBalancer!
同时,这个类是在动态代理被执行execute()的时候被调起的,所以Ribbon也是在被使用时才从Nacos获取注册表的,并不是在容器启动时!
五、Ribbon又是何时从Nacos服务端获取allServerList的?
1、我们需要跟踪ZoneAwareLoadBalancer对应的Bean的构造过程:
// com.netflix.loadbalancer.ZoneAwareLoadBalancer#ZoneAwareLoadBalancer
public ZoneAwareLoadBalancer(IClientConfig clientConfig, IRule rule,
IPing ping, ServerList<T> serverList, ServerListFilter<T> filter,
ServerListUpdater serverListUpdater) {
super(clientConfig, rule, ping, serverList, filter, serverListUpdater);
}
|
|
// com.netflix.loadbalancer.DynamicServerListLoadBalancer#DynamicServerListLoadBalancer
public DynamicServerListLoadBalancer(IClientConfig clientConfig, IRule rule, IPing ping,
ServerList<T> serverList, ServerListFilter<T> filter,
ServerListUpdater serverListUpdater) {
super(clientConfig, rule, ping);
this.serverListImpl = serverList;
this.filter = filter;
this.serverListUpdater = serverListUpdater;
if (filter instanceof AbstractServerListFilter) {
((AbstractServerListFilter) filter).setLoadBalancerStats(getLoadBalancerStats());
}
//执行远程调用,并初始化BaseLoadBalancer中的allServerList
restOfInit(clientConfig);
}
2、远程调用Nacos并初始化restOfInit()方法的逻辑:
void restOfInit(IClientConfig clientConfig) {
boolean primeConnection = this.isEnablePrimingConnections();
// turn this off to avoid duplicated asynchronous priming done in BaseLoadBalancer.setServerList()
this.setEnablePrimingConnections(false);
// 获取服务列表功能
enableAndInitLearnNewServersFeature();
updateListOfServers();
if (primeConnection && this.getPrimeConnections() != null) {
this.getPrimeConnections()
.primeConnections(getReachableServers());
}
this.setEnablePrimingConnections(primeConnection);
}
|
|
public void enableAndInitLearnNewServersFeature() {
serverListUpdater.start(updateAction);
}
这个updateAction变量是可执行的:
protected final ServerListUpdater.UpdateAction updateAction = new ServerListUpdater.UpdateAction() {
@Override
public void doUpdate() {
updateListOfServers(); // 更新Servers列表
}
};
3、updateListOfServer()方法如何从Nacos服务端获取服务列表:
// com.netflix.loadbalancer.DynamicServerListLoadBalancer#updateListOfServers
public void updateListOfServers() {
List<T> servers = new ArrayList<T>();
if (serverListImpl != null) {
// 其中的serverListImpl有三个实现,其中之一就是Nacos
servers = serverListImpl.getUpdatedListOfServers();
LOGGER.debug("List of Servers for {} obtained from Discovery client: {}",
getIdentifier(), servers);
if (filter != null) {
servers = filter.getFilteredListOfServers(servers);
LOGGER.debug("Filtered List of Servers for {} obtained from Discovery client: {}",
getIdentifier(), servers);
}
}
// 用获得到的服务列表更新BaseLoadBalancer中的allServerList
updateAllServerList(servers);
}
不用想了,肯定是NacosServerList,这个简单追踪就不赘述了!
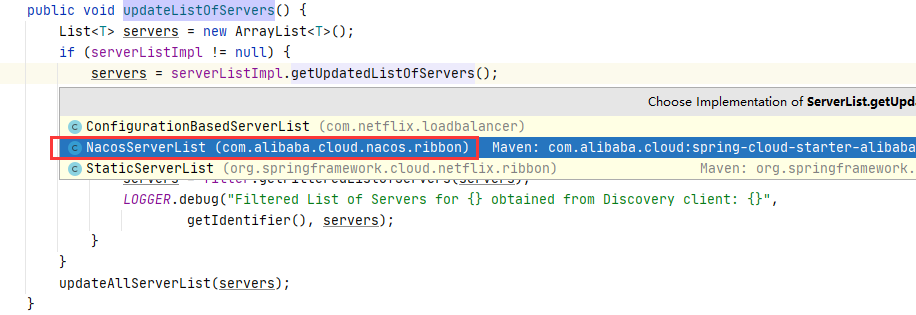
NacosServerList.getUpdatedListOfServers()最终会调用nacos客户端的核心类 NacosNamingServer.selectInstances() 方法,该方法只会返回健康实例列表;
4、根据从nacos获得到的Servers,更新本地的allServerList属性:
// com.netflix.loadbalancer.DynamicServerListLoadBalancer#updateAllServerList
protected void updateAllServerList(List<T> ls) {
// other threads might be doing this - in which case, we pass
if (serverListUpdateInProgress.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
try {
for (T s : ls) {
s.setAlive(true); // set so that clients can start using these
// servers right away instead
// of having to wait out the ping cycle.
}
setServersList(ls);
super.forceQuickPing();
} finally {
serverListUpdateInProgress.set(false);
}
}
}
|
|
public void setServersList(List lsrv) {
super.setServersList(lsrv); // 核心
List<T> serverList = (List<T>) lsrv;
Map<String, List<Server>> serversInZones = new HashMap<String, List<Server>>();
for (Server server : serverList) {
// make sure ServerStats is created to avoid creating them on hot
// path
getLoadBalancerStats().getSingleServerStat(server);
String zone = server.getZone();
if (zone != null) {
zone = zone.toLowerCase();
List<Server> servers = serversInZones.get(zone);
if (servers == null) {
servers = new ArrayList<Server>();
serversInZones.put(zone, servers);
}
servers.add(server);
}
}
setServerListForZones(serversInZones);
}
|
|
// com.netflix.loadbalancer.BaseLoadBalancer#setServersList
public void setServersList(List lsrv) {
Lock writeLock = allServerLock.writeLock();
logger.debug("LoadBalancer [{}]: clearing server list (SET op)", name);
ArrayList<Server> newServers = new ArrayList<Server>();
writeLock.lock();
try {
ArrayList<Server> allServers = new ArrayList<Server>();
...对每一个Server进行下包装...
allServerList = allServers; //本地的allServerList赋值
if (canSkipPing()) {
for (Server s : allServerList) {
s.setAlive(true);
}
upServerList = allServerList;
} else if (listChanged) {
forceQuickPing();
}
} finally {
writeLock.unlock();
}
}
到这里,总算和 二.5 章节中的allServerList进行呼应了!
至此,整个从FeignClient注解生成动态代理类LoadBalancerFeignClient;
——> Client执行时会生成ribbon下的ZoneAwareLoadBalancer类,调用nacos服务端获取服务列表;
——> 在通过ZoneAwareLoadBalancer的父类的BaseLoadBalancer.chooseServer()方法根据负载均衡算法挑选一台服务器;
——> 最后交给Feign的的Client通过URL类完成调用。
六、Feign和Ribbon的重试机制
1、首先我们做两个事情:
服务提供者feign-provider:
@GetMapping("/get/{id}")
public String getById(@PathVariable("id") String id){
System.out.println("被调用,时间:" + System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "feign-provider:com.jiguiquan.springcloud.controller.OrderController#getById=" + id;
}
服务消费者feign-consumer:
@GetMapping("test")
public String test(){
return orderService.getById("100");
}
2、不配置任何重试机制,使用默认值:
调用接口后,看服务提供者的日志(重试了2次,时间间隔为1秒):

3、我们为系统注入Feign的默认Retryer重试机制:
@Bean
public Retryer retryer(){
return new Retryer.Default();
}
再次调用,再看日志(重试了10次,):

4、Feign的默认重试器的核心代码(默认是不开启的):
public static class Default implements Retryer {
private final int maxAttempts;
private final long period;
private final long maxPeriod;
int attempt;
long sleptForMillis;
public Default() {
// 默认的重试间隔时间100ms,最大间隔时间为1s,最大重试次数为5次
this(100L, TimeUnit.SECONDS.toMillis(1L), 5);
}
// 默认下次重试间隔时间 100 * 1.5^(尝试轮次-1) 次方
// 第一次尝试:100 * 1.5(2 -1) = 150ms; 以此类推
long nextMaxInterval() {
long interval = (long)((double)this.period * Math.pow(1.5D, (double)(this.attempt - 1)));
return interval > this.maxPeriod ? this.maxPeriod : interval;
}
}
5、Ribbon和Feign的重试器的源码就不过度追溯了,直接上结论:
-
Ribbon的重试机制默认是开启的,重试1次,共调用两次;
-
Feign的Retryer重试器默认是关闭的 NEVER_RETRY;
-
Feign如果想开启默认重试器,直接在Spring容器中注入 Retryer.Default 即可,默认重试5次;
6、修改Ribbon的默认重试机制:
# Ribbon 配置 ribbon: # 单节点最大重试次数(不包含默认调用的1次),达到最大值时,切换到下一个示例 MaxAutoRetries: 0 # 0 相当于关闭ribbon重试 # 更换下一个重试节点的最大次数,可以设置为服务提供者副本数(副本数 = 总机器数 - 1),也是就每个副本都查询一次 MaxAutoRetriesNextServer: 0 # 是否对所有请求进行重试,默认fasle,则只会对GET请求进行重试,建议配置为false,不然添加数据接口,会造成多条重复,也就是幂等性问题。 OkToRetryOnAllOperations: false
7、自定义Feign重试机制(直接给 Retryer.Default 构造方法传参即可):
@Bean
public Retryer retryer(){
return new Retryer.Default(100, 1000, 3); // 调用3次(包含原本的一次调用)
}
当然,如果对 Retryer.Dafault 的默认的方法逻辑不认可,可以直接实现一个自己的CustomRetryer注入到spring容器中即可:
@Bean
public Retryer customerRetryer(){
return new Retryer() {
@Override
public void continueOrPropagate(RetryableException e) {
}
@Override
public Retryer clone() {
return null;
}
};
}